Keyhole Markup Language (KML) is a xml standard which can be used to define what and how to present geographic data in Google Earth and Google Maps. Useful examples to start can be browsed via https://developers.google.com/kml/documentation/kml_tut.
I have to display KML data in googleearth. And the KML file has to be loaded dynamically and the updates in the kml file should be shown in the googleearth on the fly.
For this we have to Create a Network Link.
Goto Add -> Network Link
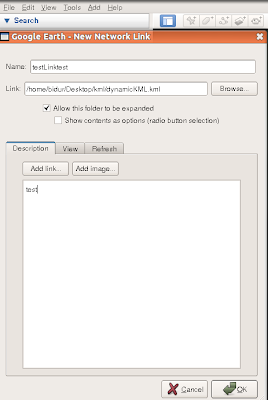
Then specify the details as shown in the figure.
To specify the frequency of updating the data, go to Refresh tab.
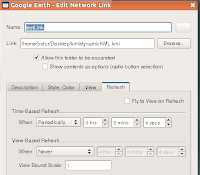
The code for dynamicKML.kml is as follows:
Note that, we are using a local file junk.kml (junk.kml and dynamciKML.kml reside in the same directory) to define the content to be displayed in the google earth interface. This can even be a remote file in which case we have to specify the remote file URL. The code for junk.kml is as follows.
Now, we can change the content of junk.kml and the changes will be seen in the google earth interface dynamically.
Comments